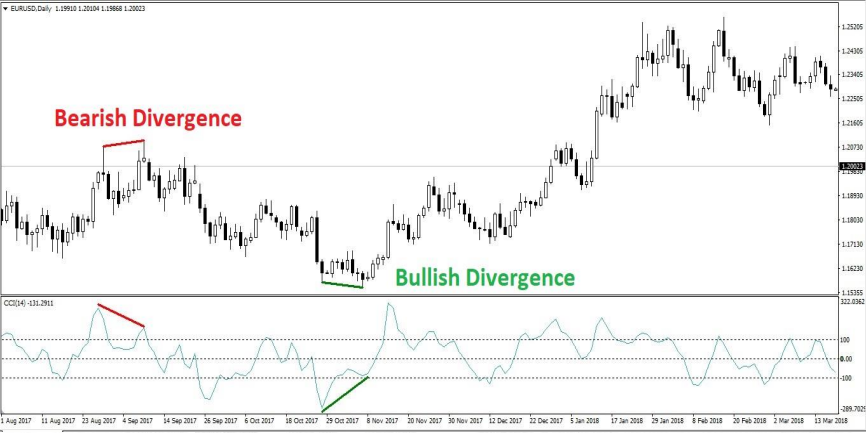
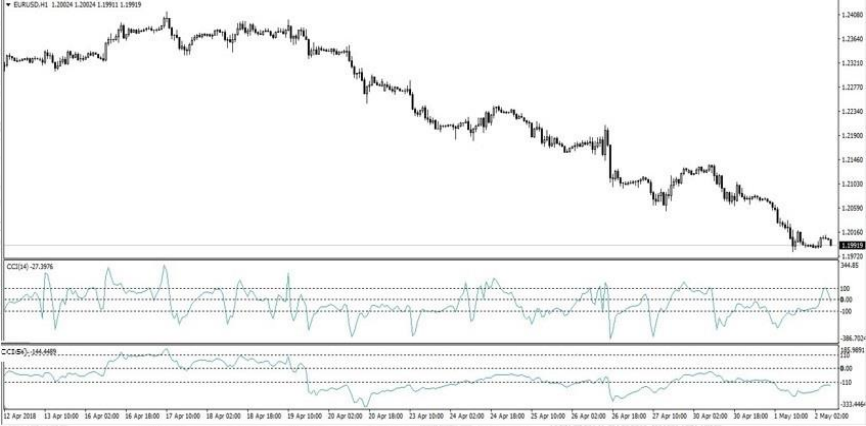
Commodity Channel Index (CCI) oscillator is a momentum based technical trading tool that was developed by Donald Lambert and featured in Commodities magazine in 1980.
Lambert originally developed CCI to identify cyclical turns in commodities, but the indicator can be successfully applied to indices, ETFs, stocks, and other securities. It is used to identify a new trend or warn of extreme conditions. It measures the change in an instrument’s price relative to a pre-defined moving average (MA) of the price divided by 1.5% of mean deviation from that average. Lambert set the constant at .015 to ensure that approximately 70 to 80 percent of CCI values would fall between -100 and +100.
CCI is relatively high when prices are far above their average. CCI is relatively low when prices are far below their average. In this manner, CCI can be used to identify overbought and oversold levels.
Commodity Channel Index (CCI) oscillator is a momentum based technical trading tool that was developed by Donald Lambert and featured in Commodities magazine in 1980.
Lambert originally developed CCI to identify cyclical turns in commodities, but the indicator can be successfully applied to indices, ETFs, stocks, and other securities. It is used to identify a new trend or warn of extreme conditions. It measures the change in an instrument’s price relative to a pre-defined moving average (MA) of the price divided by 1.5% of mean deviation from that average. Lambert set the constant at .015 to ensure that approximately 70 to 80 percent of CCI values would fall between -100 and +100.
CCI is relatively high when prices are far above their average. CCI is relatively low when prices are far below their average. In this manner, CCI can be used to identify overbought and oversold levels.


Market is Bullish
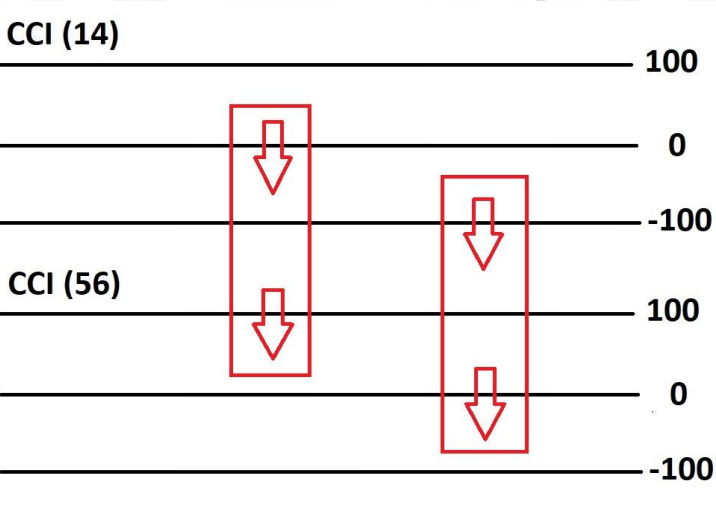
Market is Bearish
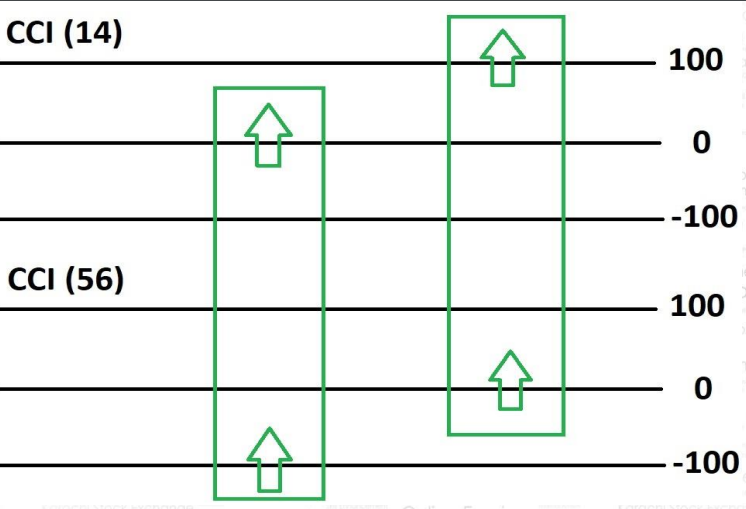
Market is Bullish
Market is Bearish


A pivot point is a technical analysis indicator which determine the overall trend of the market. The pivot point itself is simply the average of the high, low and closing price from the previous trading day. Further three Support levels (S1, S2 & S3) and three Resistance levels (R1, R2 & R3) are added to this technical analysis indicator to make it more productive in terms of taking entries & exits.
Trading above the pivot point is thought to indicate ongoing bullish sentiment, while trading below the pivot point indicates bearish sentiment.
Usually Pivot Points are calculated using previous day candle but weekly & monthly Pivot Points can be calculated using previous Week’s & previous Month’s candle for analysis to take swing positions or longer term investments.
A pivot point is a technical analysis indicator which determine the overall trend of the market. The pivot point itself is simply the average of the high, low and closing price from the previous trading day. Further three Support levels (S1, S2 & S3) and three Resistance levels (R1, R2 & R3) are added to this technical analysis indicator to make it more productive in terms of taking entries & exits.
Trading above the pivot point is thought to indicate ongoing bullish sentiment, while trading below the pivot point indicates bearish sentiment.
Usually Pivot Points are calculated using previous day candle but weekly & monthly Pivot Points can be calculated using previous Week’s & previous Month’s candle for analysis to take swing positions or longer term investments.
Third resistance (R3) = High + 2(PP – Low)
Second resistance (R2) = PP + (High – Low)
First resistance (R1) = (2 x PP) – Low
Pivot point (PP) = (High + Low + Close) / 3
First support (S1) = (2 x PP) – High
Second support (S2) = PP – (High – Low)
Third support (S3) = Low – 2(High – PP)
Note: Some indicators of charting software plots the mid points which are mini levels.
Third resistance (R3) = High + 2(PP – Low)
Second resistance (R2) = PP + (High – Low)
First resistance (R1) = (2 x PP) – Low
Pivot point (PP) = (High + Low + Close) / 3
First support (S1) = (2 x PP) – High
Second support (S2) = PP – (High – Low)
Third support (S3) = Low – 2(High – PP)
Note: Some indicators of charting software plots the mid points which are mini levels.
Weighted Pivot Point
R2 = PP + High – Low
R1 = (2 X PP) – Low
PP = (H + L + 2C) / 4
S1 = (2 X PP) – High
S2 = PP – High + Low
Median Pivot Point
R2 = PP + High – Low
R1 = (2 X PP) – Low
PP = (H + L) / 2
S1 = (2 X PP) – High
S2 = PP – High + Low
Weighted Pivot Point
R2 = PP + High – Low
R1 = (2 X PP) – Low
PP = (H + L + 2C) / 4
S1 = (2 X PP) – High
S2 = PP – High + Low
Median Pivot Point
R2 = PP + High – Low
R1 = (2 X PP) – Low
PP = (H + L) / 2
S1 = (2 X PP) – High
S2 = PP – High + Low
Bullish:
BEARISH
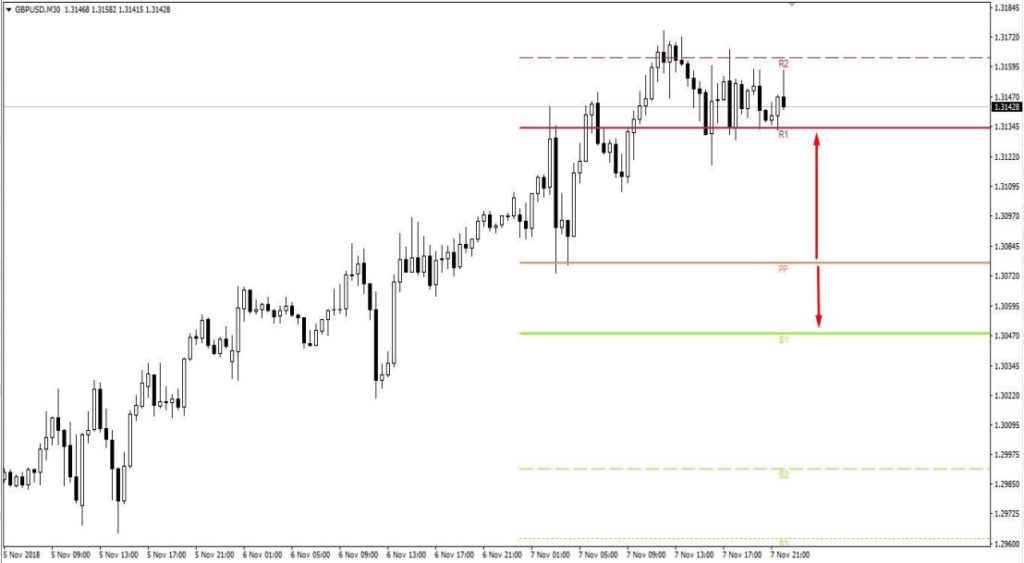
Bullish:
BEARISH

If market is trending aggressively in higher time frames.
Bullish Entry:
Bearish Entry:
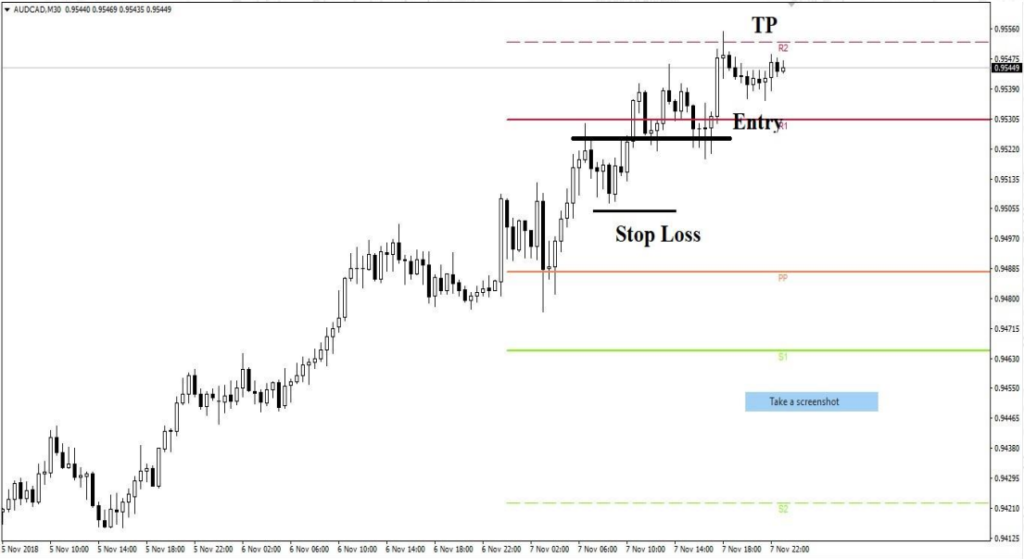
If market is trending aggressively in higher time frames.
Bullish Entry:
Bearish Entry:

If market is ranging in higher time frames
Bullish Entry:
Bearish Entry:
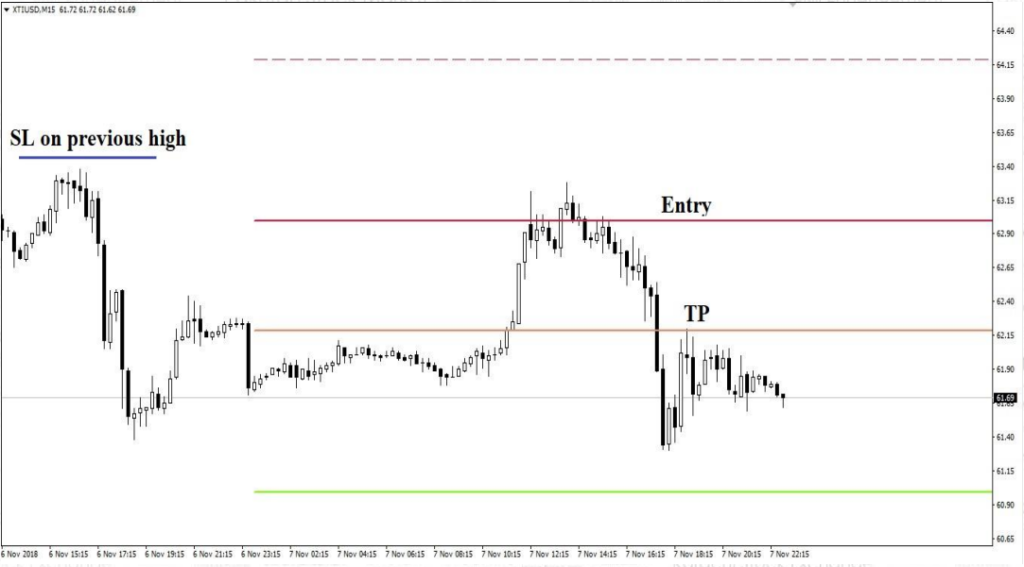
If market is ranging in higher time frames
Bullish Entry:
Bearish Entry:

It calculates the average price movement in any time frame & a useful indicator in deciding to the profit taking in running trade.
Daily Time Frame: If in daily time frame, current movement of price achieved or crossed ATR figure, it becomes an early indication that price movement has done for the day so its time to take profit.
Intra-Day Time Frame: ATR x 5 is taken as the take profit level.
It calculates the average price movement in any time frame & a useful indicator in deciding to the profit taking in running trade.
Daily Time Frame: If in daily time frame, current movement of price achieved or crossed ATR figure, it becomes an early indication that price movement has done for the day so its time to take profit.
Intra-Day Time Frame: ATR x 5 is taken as the take profit level.

